To mark its 200th anniversary, the US produced a bicentennial quarter in 1975 or 1976. A bicentennial quarter’s worth is determined by its content, rarity, and condition. The majority have a copper-nickel coating and are only worth 25 cents when in circulation. On the other hand, 40% silver quarters are significantly more valuable due to their slightly heavier weight and little “S” mintmark on the obverse. The value of a bicentennial quarter in mint condition is displayed in the most recent pricing charts.
- No mintmark (Philadelphia) copper-nickel clad: $6
- D (Denver) copper-nickel clad: $6
- S (San Francisco) copper-nickel clad proof: $4
- S (San Francisco) 40% silver uncirculated: $7.50
- S (San Francisco) 40% silver proof: $9
The bicentennial quarter, or quarter of the bicentennial, is a coin with a distinct value that may be ascertained by grade, market demand, and visual appeal; consulting an expert coin dealer is recommended.
1971 Silver Dollar Value
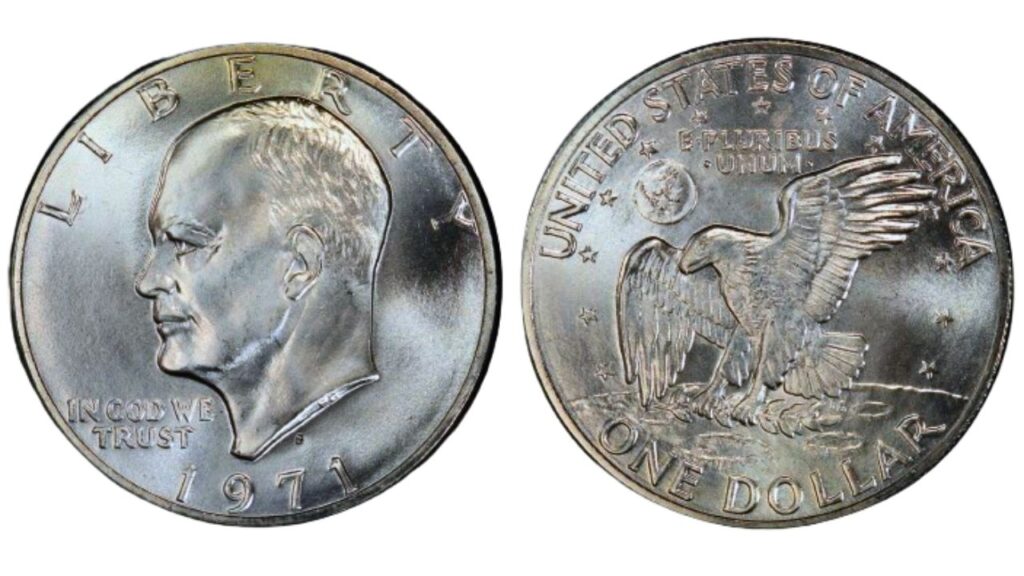

In the history of silver money, the introduction of the 1971 Eisenhower silver dollar, which bears the famous portrait of Dwight D. Eisenhower, is a momentous occasion.
1. Regular Strike 1971 Silver Dollar
- About 6.9 million coins were struck in San Francisco; in circulating condition, they ranged in value from $10 to $121, with superior quality and condition producing rarer and more costly pieces.
2. Composition and Varieties
- Coins having a copper clad core, mostly made of copper with around 20% silver mixed in, were created by the San Francisco mint. Unlike the standard striking coins, the reverse cladding (80% silver and 20% copper) produced an appealing silver tint.
3. Design and Features
- Chief engraver Frank Gasparro of the Mint drew a portrait of President Eisenhower in 1945, with an eagle on the reverse that was modeled after the Apollo 11 moon landing mission patch.
4. Proof Silver Dollars
- Over 4 million proof silver dollars were produced in San Francisco; the value of each coin varied according to its quality. While deep cameo coins range in value from $13 to $46, cameo coins, valued between $10 and $15, are highly sought after by collectors.
5. Rare Varieties and Errors
- Coins that include errors, like the 1971 silver dollar, can gain value in May. At present, the value of an oz. containing about 0.3161 oz. is $6.40.
The 1971 silver dollar is a fascinating piece of numismatic history that is a valued collection despite its condition.
1982 Penny Value:
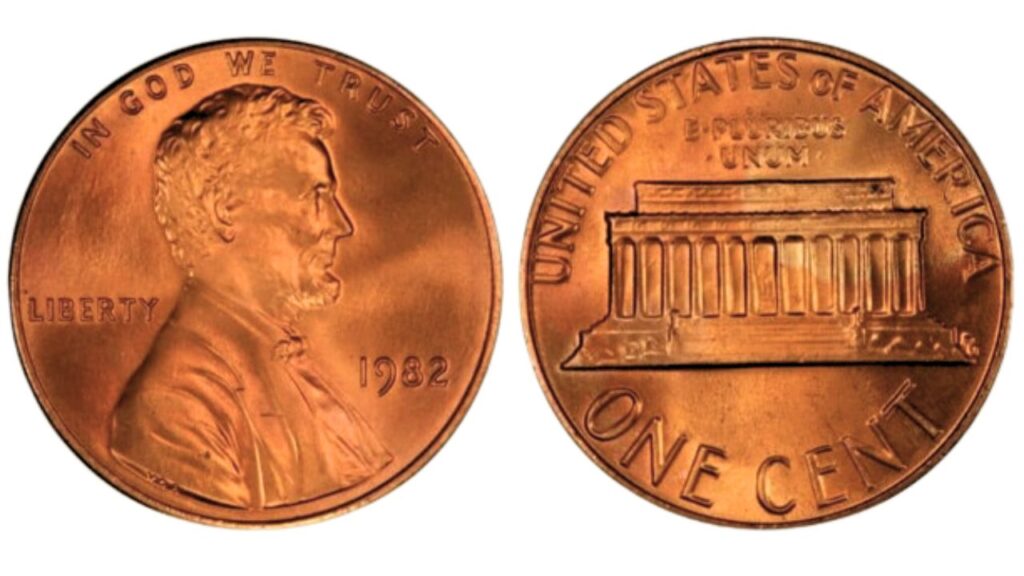

The 1982 penny’s fascinating features, which highlight its long history and varied variation, transcend its modest face value.
1. Design and Composition
- The 1982 Lincoln Penny series, which depicts Abraham Lincoln in a tuxedo and bow tie, features the Victor D. Brenner-designed Lincoln Memorial. Lincoln Memorial and the American heritage-honoring slogan “E. PLURIBUS. UNUM” are included on the reverse.
2. Composition Variations
- First Generation (Bronze) pennies, weighing 3.11 grams and measuring 19 millimeters in diameter, were composed of 95% copper and 5% zinc and tin, whereas Second Generation (Zinc-Coated Steel) pennies were composed of 95% zinc and 5% tin.
3. Varieties and Values
- Coin collectors like the 1982 “No Mint Mark” Bronze, Large Date Proof coins, which have an average circulation value of $0.05. Another highly sought-after coin is the 1982 “D” Bronze, Small Date Proof coin, which had an average circulation value of two to three cents or less. The maximum price for the Small Date Bronze Penny is $3,5003.
1969 Penny Value:
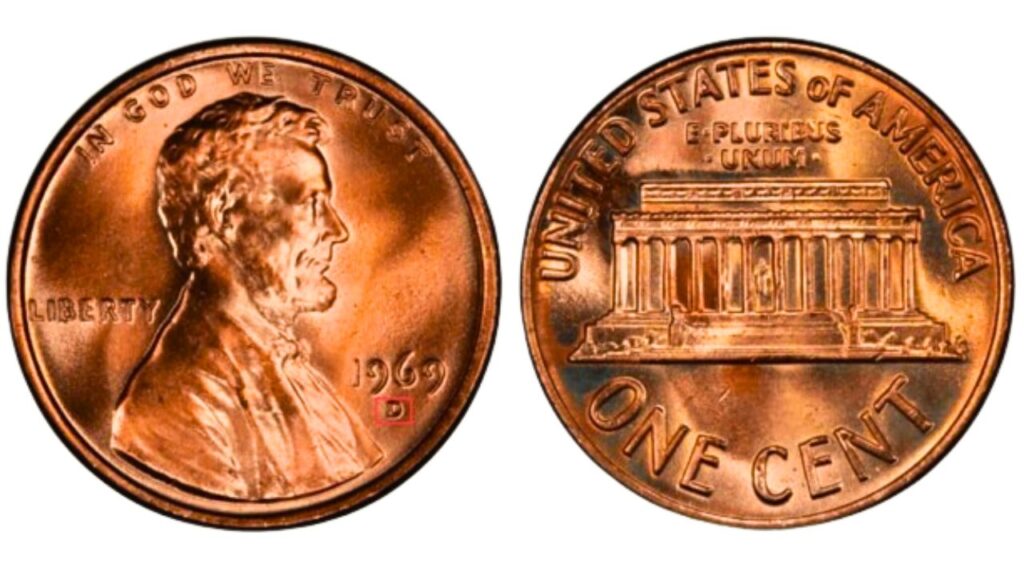

The curious coin, a 1969 penny, has a mint mark that adds to its intriguing qualities and may include inaccuracies.
1. Composition and Common 1969 Pennies
- The composition of pre-1982 Lincoln cents is 95% copper and 5% zinc. The majority of 1969 Lincoln cents are worth around two cents each because to their high copper content and metal value.
2. The Valuable 1969 Doubled Die Penny
- One of the rarest and most precious coins in the world, the 1969 doubled die penny may be valued over $25,000, much above its face value.
3. Specific Varieties and Values
- 1969 Penny:
- Minted: 1,136,910,000 (1.3 billion).
- Value: 25 to 50+ cents.
- 1969-D (Denver) Penny:
- Minted: 4,002,832,200 (4 billion).
- Value: 20 to 40+ cents.
- 1969-S (San Francisco) Penny:
- Minted: 544,375,000.
- Value: 40 to 60+ cents.
- 1969-S Proof Penny:
- Minted: 2,934,631.
- Value: 70 cents to $1+.
- 1969-S Doubled Die Penny:
- Mintage unknown.
- Value: $25,000+.
4. Grading Matters
- The U.S. Coin Grading Standards state that a coin’s worth may be precisely determined with a coin magnifier.
Even though 1969 pennies are only worth two cents, there is a sought-after doubled die penny worth potentially finding a buried treasure.
1976 Penny Value:

One of the most valuable pieces of American currency is the penny, which honors the bicentennial celebrations of the Declaration of Independence.
1. 1976 Penny Value Chart
- In 1976, proof coins from Philadelphia were valued at $0.02 apiece, whereas uncirculated coins from Denver and Philadelphia were valued at $1 each. West Point mint pennies are worthless, whereas proof coins from San Francisco are worth $3.20.
2. Features of the 1976 Penny
- The 1976 penny’s reverse design showcases Frank Gasparro’s Lincoln Memorial, a distinctive element in bicentennial coins, while the obverse design includes President Lincoln’s bust, the mint mark, and the year 1976.
3. Rare Varieties and Values
- Lincoln’s uncirculated pennies, worth ten to twenty cents, and proof pennies from 1976, valued at $1 to $2 apiece, make excellent investments. In an auction in 2014, the record-holding MS68RD graded 1976 Lincoln cent brought $7,931.25.
1976 pennies are used to commemorate the bicentennial of American history—a historical artifact that might not necessarily provide financial gain.
1956 Penny Value:
A penny’s worth fluctuates greatly based on its mint status, which is determined by different types and mint markings.
1. 1956 No Mint Mark Penny (Philadelphia)
- Coins in circulating condition were valued at $0.02 each, and the Philadelphia Mint produced large amounts of them. Mint State coins are very sought after by collectors, as they were never circulated and may bring up to $1 for uncirculated specimens.
2. 1956-D Penny (Denver)
In 1956, the Denver Mint produced 1,098,210,100 cents, which was the greatest output value for the wheat cent series. For collectors, especially the younger and novice ones, circulating 1956-D pennies are valued because of the Lincoln’s prominent features and powerful wording on the reverse.
3. Values
Depending on its condition
- You may exchange a 1956 No Mint Mark penny for anything from $0.02 to $5 or more.
- Uncirculated, very excellent variations may sell for more than $100.
- If the 1956-D penny is not in uncirculated form, which collectors could find more desirable, it is usually worth its face value.
1956 pennies are interesting artifacts of numismatic heritage and have historical relevance despite their lack of wealth.
1960 Penny Value:

The 1960 pennies is an interesting coin with special qualities that make it much more valuable.
1. 1960 Penny Value Chart
- 1960 (P) No Mint Mark Large Date Penny
- In MS63: Around $4.
- In MS65: Approximately $14.
- In MS67: Valued at $360.
- 1960 (P) No Mint Mark Small Date Penny
- In MS63: About $6.
- In MS65: Around $20.
- In MS67: Fetches $550.
- 1960 D Large Date Penny
- In MS63: Approximately $8.
- In MS65: Valued at $16.
- In MS67: Worth $475.
- 1960 D Small Date Penny
- In MS63: About $10.
- In MS65: Approximately $22.
- In MS67: Valued at $340.
2. Proof Penny Values
- 1960 (P) No Mint Mark Large Date Proof Penny
- PR60: Around $5.
- PR65 (Cameo): Approximately $30.
- PR69 (Deep cameo): Valued at $130.
- 1960 (P) No Mint Mark Small Date Proof Penny
- PR60: About $6.
- PR65 (Cameo): Around $50.
- PR69 (Deep cameo): Fetches $625.
3. History of the 1960 Penny
- The 1960 pennies’ Lincoln Memorial design, created by Frank Gasparro, was featured on the coin for fifty years. In 1960, Denver produced the majority of the nearly 2 billion pennies that were struck in Philadelphia. Both big and tiny date coins were among the variations
4. Features of the 1960 Penny
- Abraham Lincoln is shown in the Lincoln Memorial, which is a distinctive and iconic depiction of the President that highlights his contributions to American history and legacy.
5. Interesting Errors
- The Mint made a few interesting mistakes in manufacturing.
The 1960 pennies have historical value and numismatic appeal even if they aren’t very valuable.
Value of $2.00 bill 1976:

The 1976 Bicentennial Two, popularly referred to as the two-dollar note, has an interesting past and variable values that are impacted by a number of variables.
1. Design and Changes
- The 1976 two-dollar note was reprinted by the US government as a Federal Reserve Note in green, with the Declaration of Independence rather than Thomas Jefferson’s Monticello home on the reverse.
2. Value
- Considering that more than 500 million 1976 two-dollar notes were issued, their rarity is not very high. While uncirculated notes might sell for $9–15, regularly circulated notes are only about $2. Low serial numbers are one factor that might increase value
3. Stamped Bills
- Since the series’ debut printing on April 13, 1976, stamped banknotes with a distinct city name are worth a little more, particularly for first-day issues.
4. Star Notes
- Federal Reserve Banks of Kansas City and Minneapolis are offering rare star notes valued at around $80 (fine) and $150 (uncirculated, MS 63 grade), whereas common star notes are valued at $8 in fine condition and $20–25 in uncirculated.
5. Error Bill
- The serial number is positioned on the top right and bottom left of the series, which is a noticeable mistake.
1976 two-dollar notes are interesting collectors and have historical value even if they are not particularly valuable.
What is the history of US currency?

The nation’s economic upheavals, technical developments, and people’s tenacity are all reflected in the history of US money. By virtue of the Coinage Act of 1792, the first official U.S. coins were struck in that year. During the 1800s, notable Americans like Andrew Jackson, Abraham Lincoln, and Alexander Hamilton were featured on banknotes, which encouraged the issue of more paper money during the Civil War.
Legal Tender Notes, or “greenbacks,” were introduced by the US Treasury in 1861 as fiat money that was not backed by gold or silver. The Federal Reserve System was founded in 1914 as a result of the establishment of the National Banking System in 1863. In 1914, Federal Reserve Notes were adopted as the norm for printed money.
How do I know if my bill is valuable?

A bill’s worth can be ascertained using a number of methods, including as its serial number, seals and dates, star notes, mint mistakes, Federal Reserve Bank letters and numbers, and internet resources. A fancy serial number checker can assist in determining whether your bill qualifies, and fancy serial numbers can greatly boost a bill’s value. Checking the year and seal color on your bill will help you evaluate its value.
Older bills with red, brown, or blue seals manufactured between 1862 and 1917 are typically regarded rarer. Uncirculated bills fetch greater values, while banknotes in exceptional condition are worth more. Replacement notes bearing a star before the serial number are called star notes, and collectors find them to be more desirable. Misaligned or incorrectly printed bills may also
Are there any other rare bills from 1976?
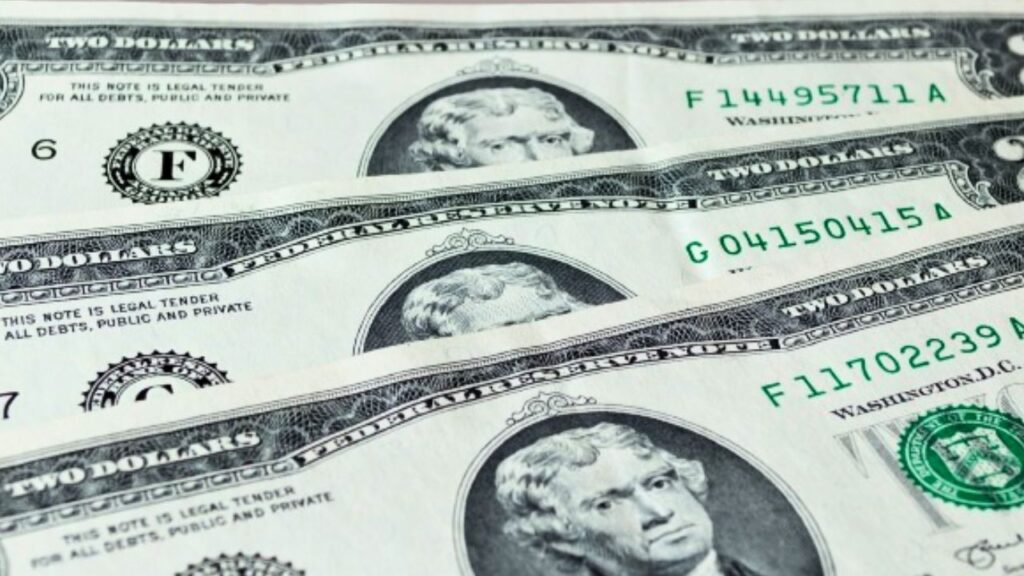

Significant events like the 1976 United States Bicentennial celebration have an impact on the value of different notes and coins. The face value of a typical 1976 $2 note is $2, however uncirculated bills can sell for as much as $15. A few notes bore the date “APR 13, 1976,” signifying that they were special editions commemorating the occasion. For collectors, these notes have sentimental significance. Replacement notes that include a star before the serial number, or “star notes,” are frequently worth more to collectors.
Uncirculated star notes may be more valuable than circulated ones, which can only be valued at about $8. Miscuts and multiple serial numbers are examples of printing defects that are highly unusual and valuable. The value of bills with distinct serial numbers on the top and bottom is around $400.
